-
- Contact Us
- Privacy Policy
- term and condition
- Cookies policy
R201L00010W Specs & Stock Report: Performance, Sourcing
The R201L00010W delivers industry-grade RF performance suitable for high‑frequency PCB designs. Point: its datasheet specifies operation to 65 GHz. Evidence: manufacturer datasheet and distributor spec pages report insertion loss as low as 0.12 dB at typical test points. Explanation: that combination of bandwidth and low loss positions the part for demanding test and module applications where signal integrity is critical.
Point: this report compiles technical highlights, test guidance, and a US sourcing playbook. Evidence: consolidated technical fields and recommended procurement checks reflect common engineering acceptance criteria. Explanation: procurement and engineering teams can use the contained RF test templates, inventory checks, and sourcing controls to speed qualification while mitigating counterfeit and lead‑time risk.
R201L00010W Overview & Key Specs
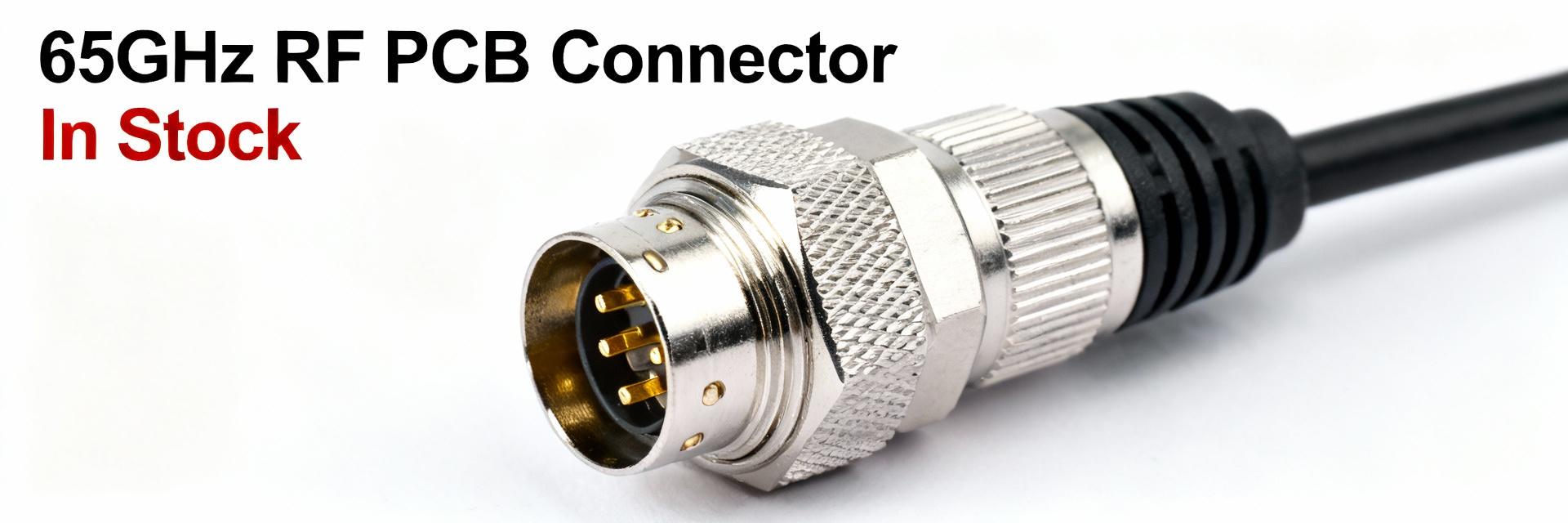

Product family & intended applications
Point: the device is an SMPM‑LOCK style PCB receptacle with limited detent, intended for high‑frequency test, RF modules, aerospace, and telecom applications. Evidence: form factor and mating style enable compact board integration and repeatable test points. Explanation: designers choose this family where 50 ohm impedance stability, small footprint, and frequent mating are required for calibration jacks and module interfaces.
Core specs to present (datasheet snapshot)
Point: key mandatory fields must be captured verbatim from the technical datasheet. Evidence: frequency max: 65 GHz; insertion loss: 0.12 dB (at specified frequency); impedance: 50 Ω; insulation resistance: 5 GΩ; mating cycles: 500; max operating temp: +165°C; contact/shield termination: solder. Explanation: including units and tolerances enables direct comparison and qualification in procurement and incoming inspection records.
Detailed Electrical & Mechanical Analysis
Electrical performance to analyze
Point: report measurable RF parameters during qualification. Evidence: measure insertion loss vs frequency, S‑parameters to the connector limit, return loss/VSWR, isolation, DC insulation and contact resistance. Explanation: these metrics validate that the part meets system budgets; typical thresholds to flag include return loss better than −20 dB below X GHz and insertion loss within datasheet tolerance across the band.
Mechanical & environmental characteristics
Point: examine materials, mounting style, and robustness. Evidence: typical construction uses beryllium copper contacts with conductive plating and solder termination; mounting may be surface mount or board edge dependent. Explanation: material and plating thickness (µm) affect wear and corrosion resistance, while mating cycles and thermal limits guide assembly and vibration qualification for aerospace or telecom deployments.
Test Data & Real‑World Performance Indicators
Recommended lab tests & metrics to include
Point: define standardized lab procedures for repeatable qualification. Evidence: perform network analyzer S‑parameter sweeps to the connector rated GHz, insertion and return loss plots, temperature cycling and pre/post mate contact resistance. Explanation: expected pass/fail criteria should map to datasheet values plus a margin; record raw S‑parameter files and lot traceability for acceptance.
Field reliability and failure modes
Point: common failures stem from mechanical wear and environmental stress. Evidence: observed modes include contact wear from repeated mating, solder‑joint fatigue, and plating degradation under corrosive conditions. Explanation: enforce handling procedures, visual and electrical inspection after assembly, and limit mate cycles in service or schedule preventative replacement when deployed in harsh environments.
Stock & Availability Report (US Distributors)
Current stock snapshot — how to compile
Point: compile live inventory and pricing snapshots from authorized US distribution channels. Evidence: capture SKU, stock quantity, lead time, MOQ, and landed cost into a tracking spreadsheet with timestamps. Explanation: use standardized long‑tail search queries for stock checks and record multiple authorized sources to triangulate availability and detect anomalies in supply.
Price, lead‑time trends & procurement flags
Point: track price and lead‑time movement over rolling windows. Evidence: compare 30/90/180‑day snapshots to surface trends and flag rapid increases or persistent shortages. Explanation: procurement flags include unusually low pricing, nonstandard packaging, or inconsistent traceability—use negotiation levers like minimum order, alternates, or consignment agreements to reduce exposure.
Sourcing & Alternatives Strategy
Authorized vs gray‑market sourcing — risk matrix
Point: verify distributor authorization and traceability before purchase. Evidence: require COA/COC, country‑of‑origin, and lot trace documents; perform sample functional tests. Explanation: red flags include missing documentation, nonstandard labels, or seller reluctance to provide samples; contractual protections should mandate lot traceability and return rights.
Alternative parts & cross‑reference candidates
Point: identify functional equivalents by matching impedance, frequency rating, and mating style. Evidence: build a shortlist of 3–5 candidates with comparable insertion loss @ target GHz, mating cycles, and thermal range. Explanation: evaluate footprint and solder process compatibility and plan requalification testing (S‑parameters, mechanical durability) before design swaps.
Procurement & Engineering Action Plan
RFQ & engineering spec checklist
Point: standardize RFQ content to avoid ambiguity. Evidence: include exact part number, datasheet revision, required lot traceability, test requirement list (S‑parameters to specified GHz, mate‑cycle proof), packaging and handling. Explanation: specify minimum acceptance tests and sample counts for incoming inspection to catch nonconforming lots early.
Implementation: PCB footprint, assembly, and inventory practices
Point: align PCB land pattern and assembly controls with the connector’s tolerance notes. Evidence: follow footprint sensitivity and solder fillet recommendations; define ESD, cleaning, and storage (temperature/humidity) rules. Explanation: maintain safety stock based on lead‑time variability, vendor qualification, onshore buffer stocking, and emergency alternates to sustain production.
Summary
- R201L00010W combines up to 65 GHz bandwidth with low insertion loss; verify datasheet fields (frequency, insertion loss, impedance) during incoming inspection and include the part number in RFQ language to ensure traceability.
- Standardize lab S‑parameter sweeps, temperature cycling, and mate‑cycle checks as pass/fail gates; retain raw test files and lot IDs for field traceability and failure analysis.
- Maintain a multi‑source stock snapshot from authorized channels, use contractual lot traceability, and qualify 3–5 cross‑reference candidates to reduce lead‑time and counterfeit risk.
FAQ
What are the critical specs to confirm for R201L00010W before acceptance?
Confirm the maximum frequency rating, specified insertion loss at the referenced frequency point, 50 Ω impedance, insulation resistance value, mating cycle rating, maximum operating temperature, and termination style. Require datasheet revision and lot traceability; perform baseline S‑parameter checks and contact resistance verification on sample pieces before bulk acceptance.
How should procurement monitor stock and detect supply risk for R201L00010W?
Use timestamped inventory snapshots from multiple authorized channels, track 30/90/180‑day price and lead‑time trends, and flag sudden availability drops or anomalous low prices. Negotiate minimum orders, consignment, or safety stock and demand trace documentation to mitigate counterfeit and gray‑market exposure.
What test scope is recommended to qualify equivalents to R201L00010W?
Run full S‑parameter sweeps to the target GHz, insertion and return loss plots, contact resistance before/after mating cycles, thermal cycling and vibration as applicable. Compare insertion loss and return loss against the target part at key frequencies and require mechanical durability tests to match the mating cycle specification.
- Technical Features of PMIC DC-DC Switching Regulator TPS54202DDCR
- STM32F030K6T6: A High-Performance Core Component for Embedded Systems
- APT50GH120B Datasheet Deep Dive: Specs, Ratings & Curves
- APT50GH120BSC20 Power Module: Latest Performance Report
- APT50GH120BD30 IGBT: How to Maximize Efficiency for EV Drive
- GTSM20N065: Latest 650V IGBT Test Report & Metrics
- CMSG120N013MDG Performance Report: Efficiency & Losses
- GTSM40N065D Technical Deep Dive: 650V IGBT + SiC SBD
- NOMC110-410UF SO-16: Live Stock & Price Report
- 1757255 MSTBA 5.08mm PCB: Step-by-Step Install & Solder
-
 EXB-V4V120JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 12 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V120JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 12 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V473JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 47K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V473JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 47K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V823JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 82K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V823JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 82K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V151JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V151JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V181JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 180 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V181JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 180 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V331JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 330 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V331JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 330 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V152JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 1.5K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V152JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 1.5K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V563JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 56K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V563JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 56K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V104JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 100K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V104JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 100K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V154JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V154JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150K OHM 0606