Point: A meta-review of typical SMB entries shows SMB-style 50 Ω coaxial connectors specified for DC–4 GHz with tight VSWR and compact PCB-mount variants tailored to space-constrained RF designs. Evidence: manufacturer datasheet fragments and quick-reference guides consistently list these baselines. Explanation: This article uses that context to extract the critical electrical, mechanical and integration details engineers need to specify, test, and deploy confidently; it references the 6-1337482-0 and the RF SMB connector family for clarity.
Point: Readers need an immediately actionable summary of what to verify on a datasheet. Evidence: common procurement and test failures stem from overlooked footprint, plating, or VSWR limits reported in the datasheet. Explanation: The introduction sets expectations: capture physical form, impedance/frequency envelope, S-parameters, and mechanical lifetime before specifying samples or production runs.
1 — Technical overview and connector family context (Background)
1.1 Connector type & form factor
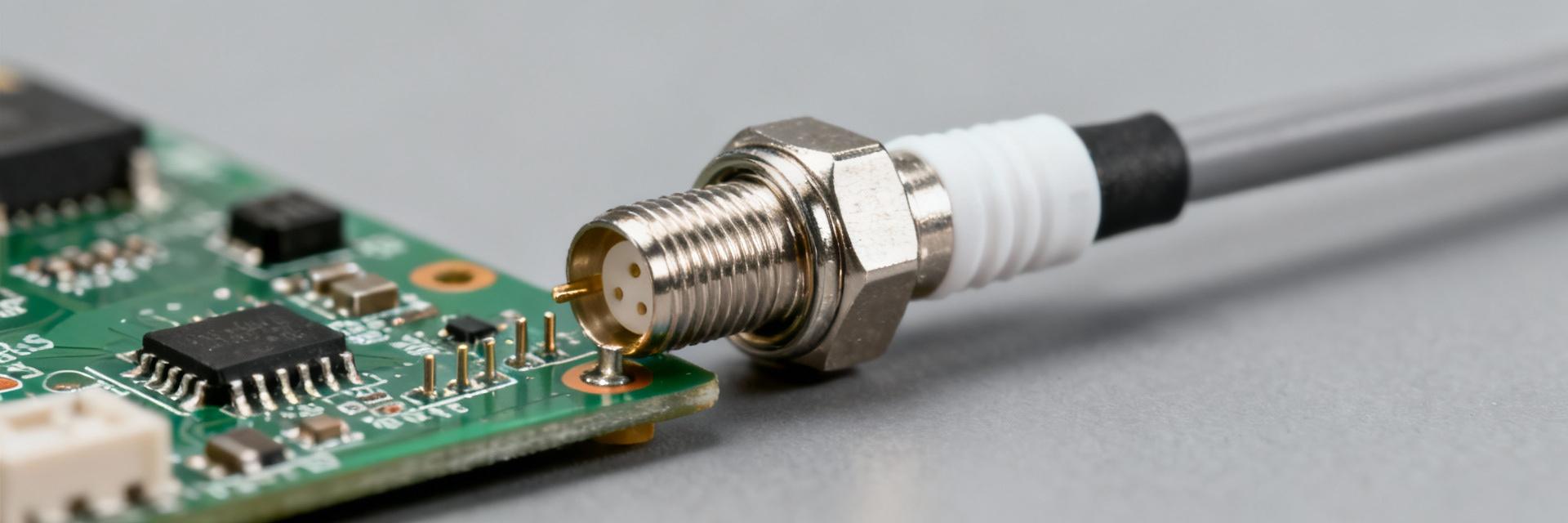
Point: The SMB style is a snap-on subminiature coaxial connector optimized for quick mating and compact footprints. Evidence: Typical SMB PCB jacks present short overall length, mated outer diameters near subminiature sizes, and either through-hole or surface-mount terminations. Explanation: For footprint planning, engineers should confirm whether the part is a jack or plug, straight or right-angle, and note the SMB PCB jack dimensions on the manufacturer drawing for clearance and assembly.
1.2 Electrical baseline: impedance, coupling, and typical frequency ranges
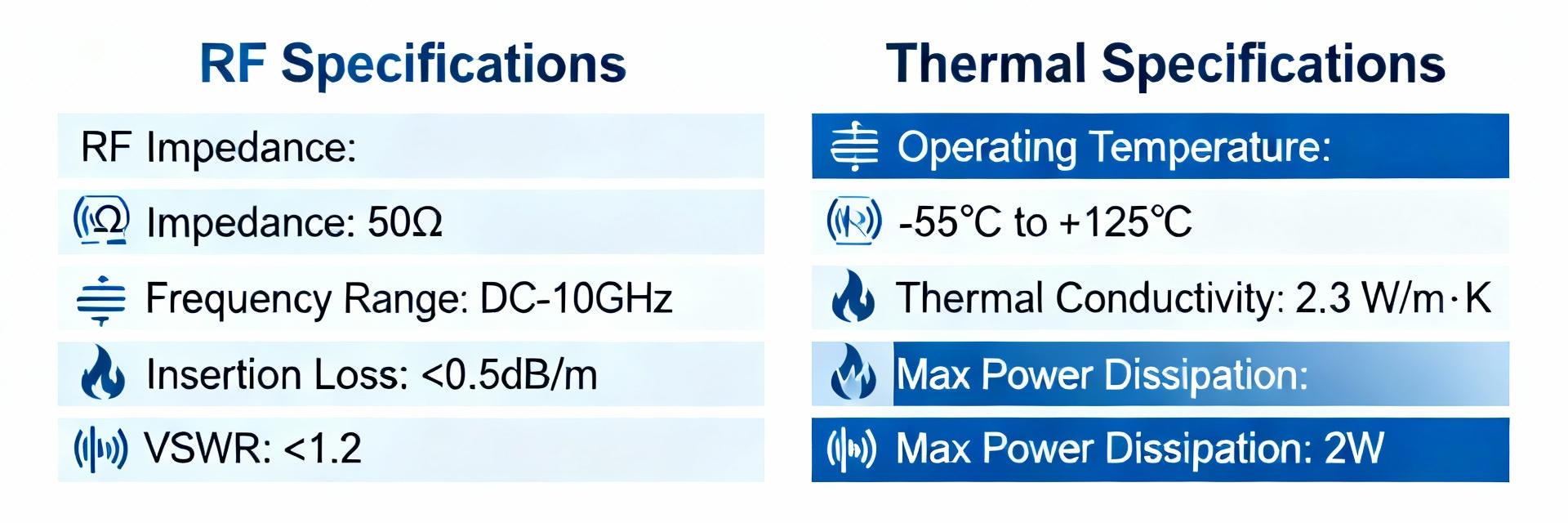
Point: SMB connectors are specified to 50 Ω nominal and commonly rated to DC–4 GHz as a baseline, with snap-on coupling impacting repeatability. Evidence: Datasheet fields to read first include impedance, frequency range, and VSWR/return loss across the band. Explanation: Comparing SMB to neighboring classes (e.g., SMA, SMC) shows trade-offs: SMB favors compactness and speed of mate/demate over the threaded coupling and marginally higher frequency ceiling of other classes.
2 — Datasheet parameter deep-dive (Data analysis)
2.1 Mechanical specifications: materials, finishes, tolerances
Point: The 6-1337482-0 datasheet will list body material, dielectric, center contact alloy, plating, torque or retention specs, and mating life. Evidence: Typical values include brass or beryllium copper bodies, PTFE dielectrics, gold-plated center contacts and nickel over brass shells with specified mating cycles. Explanation: Extract each field and compare to assembly and environment requirements—materials determine solderability, corrosion resistance, and wear under cyclic mating.
ParameterDatasheet valueTest conditionPass/Fail threshold
Body materialBrass / Ni platingAs shippedNo visible corrosion
Center contactBeCu / Au flashContact resistance test<10 mΩ
Mating cycles500 cyclesRoom temp, dryNo mechanical failure
2.2 Electrical specifications: insertion loss, VSWR/return loss, power handling
Point: Key electrical parameters are insertion loss (S21), VSWR/return loss (S11), DC resistance, and power handling across the declared band. Evidence: Datasheets provide S-parameter points or curves, maximum insertion loss per frequency, and VSWR limits; test conditions often indicate temperature and fixture type. Explanation: Capture both typical and maximum values, note the test fixturing that can mask connector discontinuities, and flag any derating with temperature or frequency.
3 — Performance testing & validation (Data analysis / Method)
3.1 Recommended test setups and measurement methods
Point: Validation requires calibrated VNA measurement with appropriate fixtures and de-embedding; SOLT calibration to the connector interface is recommended. Evidence: Best practice uses short cables/fixtures, calibration standards at the connector plane and fixture de-embedding to remove board or adapter effects. Explanation: For PCB-mounted SMB, include a mate/demate sequence in test plans, sweep beyond the claimed band to observe resonances, and record fixture notes so test results are reproducible.
3.2 Typical acceptance criteria and troubleshooting signals
Point: Acceptance criteria should be defined from datasheet claims with margin—example VSWR <1.5 up to DC–4 GHz, insertion loss <0.2 dB at low GHz. Evidence: Common failure modes are solder joints, plating wear, or misalignment causing elevated return loss. Explanation: Troubleshoot with visual inspection, continuity checks, and swept return loss; isolate mechanical issues by swapping mating halves and verifying contact resistance under load.
4 — Design and PCB integration guidelines (Method)
4.1 PCB footprint, mechanical mounting and soldering recommendations
Point: Footprint guidance should come from the mechanical drawing: land pattern, hole size for through-hole, and solder fillet expectations. Evidence: Manufacturer mechanical drawings specify keepout, reference plane cutouts and recommended solder fillet heights for reliable joints. Explanation: For SMT SMBs use solder fillet acceptance criteria, avoid excessive reflow temperatures on plated contacts, and request sample reflow curves if contact plating or dielectric is temperature-sensitive.
4.2 Impedance control, grounding and RF layout best practices
Point: Controlled-impedance trace routing, reference plane continuity and ground via placement near the connector are essential to preserve VSWR. Evidence: Layout notes typically call for a continuous ground plane under the connector and multiple ground vias adjacent to mounting pads. Explanation: Maintain a solid reference plane up to the connector rear, minimize discontinuities, and ensure sufficient clearance to avoid stray capacitance that degrades return loss.
5 — Applications and selection criteria (Case)
5.1 Common system-level applications and environment suitability
Point: SMB variants like this part are common in compact RF modules, test jacks, short-run cable assemblies and handheld wireless devices. Evidence: Datasheets include environmental limits—operating temperature range, vibration and shock ratings—that determine suitability. Explanation: Confirm mechanical retention and plating for field devices where frequent mating occurs; for test environments, prioritize robust mating cycles and low insertion loss.
5.2 How to choose the right variant and alternatives
Point: A decision checklist helps select correct variant: required frequency, power handling, mating cycles, PCB space and retention type. Evidence: Substitutions must be checked for pinout, footprint, and equivalent electrical performance to avoid rework. Explanation: When substituting, compare mechanical drawings, S-parameter plots and mating instructions; request a sample for electrical validation to avoid surprises in production.
6 — Procurement, compliance and datasheet verification checklist (Action)
6.1 Datasheet verification checklist before purchase
Point: Procurement should verify part number, footprint drawing, electrical specs at required frequency, mechanical drawing, material/finish, mating instructions and packaging. Evidence: A concise verification table simplifies supplier responses and internal sign-off prior to ordering. Explanation: Capture each verified field against the manufacturer reference and test evidence; include a sample request clause so procurement secures validation parts for VNA testing before full buys—record this in the 6-1337482-0 datasheet pinout verification.
FieldVerified value
Part numberConfirmed matches assembly
FootprintMechanical drawing matched
ElectricalVSWR / IL at required band
6.2 Compliance, life-cycle and sourcing tips
Point: Confirm RoHS/REACH declarations, lot traceability and whether the part is current or superseded. Evidence: Manufacturers often publish qualification reports and change notices that affect long-term sourcing. Explanation: Procurement tactics include requesting samples, confirming lot traceability for automated assembly, and specifying packaging suitable for pick-and-place to reduce assembly risk and ensure consistent yield.
Summary
Verify impedance, frequency and S-parameters on the manufacturer datasheet before specifying the 6-1337482-0 part for any 50 Ω RF path; validate with VNA measurement against claimed VSWR and insertion loss.
Confirm mechanical drawings and SMB PCB jack dimensions for footprint, mounting and solder fillet expectations to prevent assembly failures and ensure repeatable performance in compact RF designs.
Use a calibrated SOLT VNA setup with fixture de-embedding and a defined mate/demate protocol to reproduce datasheet results and catch plating or tolerance issues early.
FAQ
What should be checked first on the RF SMB connector datasheet?
Point: First check impedance, frequency range and VSWR/return loss. Evidence: These electrical fields determine RF compatibility and are commonly listed near the datasheet header. Explanation: Confirm these values against system requirements, and if margins are tight, request S-parameter data and physical samples for VNA validation prior to procurement.
How can engineers validate the 6-1337482-0 performance for production?
Point: Validate with calibrated VNA sweeps, fixture de-embedding and mate/demate cycles. Evidence: Acceptance criteria should map to datasheet claims with defined margins for VSWR and insertion loss. Explanation: Include mechanical inspections, contact resistance checks and environmental spot tests as part of incoming quality to ensure production units match validated samples.