-
- Contact Us
- Privacy Policy
- term and condition
- Cookies policy
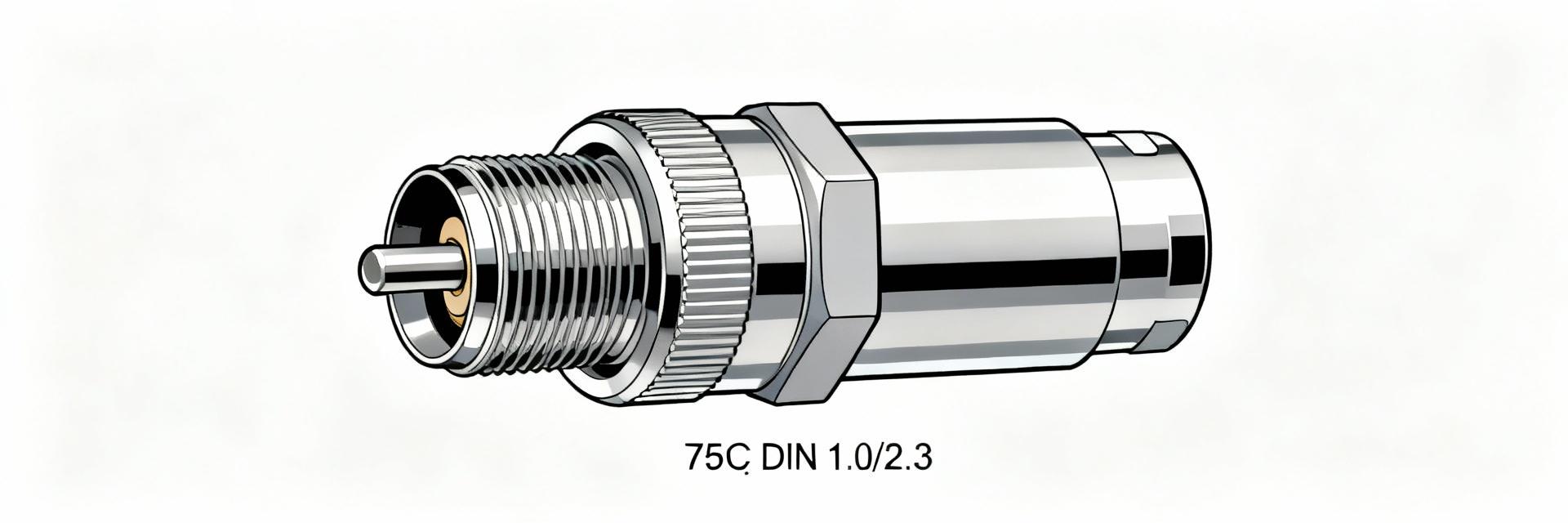
60K131-815N1 Rosenberger Datasheet: 50 Ohm 7/16 Jack
The Rosenberger 60K131-815N1 is specified as a 7/16 straight jack for 50 Ohm systems, rated DC to 7.5 GHz per the manufacturer datasheet. This page summarizes the core specs, explains RF and mechanical performance implications, gives mounting and procurement guidance, and lists quick install and troubleshooting actions for engineers working with this 50 Ohm 7/16 jack.
1 — Product overview and key specifications (background)
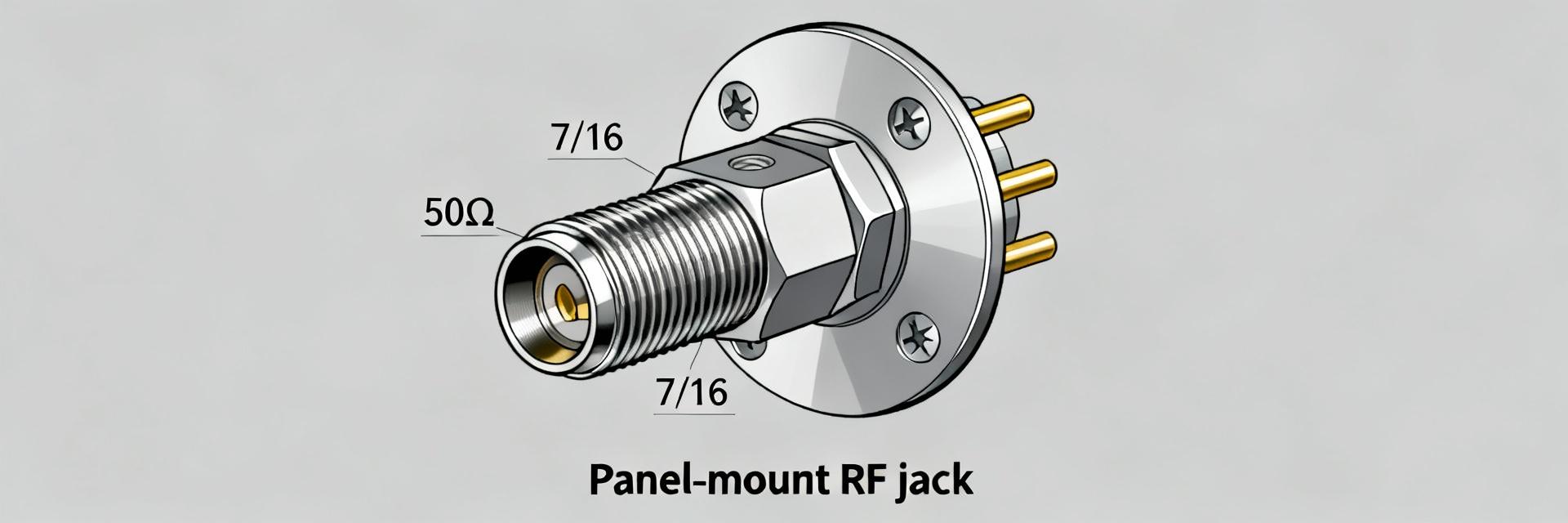
What the part is (one-sentence definition + key identifiers)
Point: The 60K131-815N1 is a Rosenberger 7/16 straight jack designed for 50 Ω RF systems. Evidence: Datasheet identifies the part number, connector type and frequency rating (DC–7.5 GHz). Explanation: Use it where robust, low-intermod, higher-power coax connections are required—common in base stations, broadcast and antenna feedlines.
At-a-glance spec table (what to show and why)
- Impedance: 50 Ω — fundamental for system matching and link-budget calculations.
- Frequency range: DC – 7.5 GHz — datasheet-stated usable band.
- VSWR / Return loss: see datasheet plots — include typical and maximum curves for design checks.
- Insertion loss: datasheet/test points — list if provided for your assembly frequencies.
- Contact finish: specified on datasheet (e.g., silver or alternative) — affects conductivity and corrosion resistance.
- Mounting style: panel-mount straight jack with specified thread and cutout drawing.
- RoHS / lead-free: stated compliance on the datasheet.
- Materials & operating temp: body and contact materials plus operating range (consult datasheet drawing).
2 — Electrical and RF performance (data analysis)
Measured / datasheet RF parameters to explain
Point: RF plots in the datasheet show return loss and VSWR behavior across DC–7.5 GHz. Evidence: Typical return-loss curves and VSWR traces appear in the official specification; the datasheet distinguishes typical vs. maximum values and test conditions. Explanation: For accurate link-budget or insertion-loss budgeting, extract S-parameter points at your operating frequencies and use the datasheet’s specified maxima for worst-case calculations.
How performance affects system design (practical implications)
Point: VSWR and insertion loss drive delivered power and reflected energy. Evidence: Higher VSWR increases mismatch loss and potential heating; insertion loss reduces available transmit power. Explanation: Choose this 7/16 jack when low intermodulation and power handling are priorities; verify S11/S21 on the assembled cable using network-analyzer sweeps and verify torque/mating to reproduce datasheet performance.
3 — Mechanical, materials & environmental data (method/guideline)
Mechanical dimensions & mounting instructions
Point: Mechanical drawings define panel cutout, thread, mating depth and tolerances. Evidence: The datasheet includes a dimensional drawing and recommended panel cutout. Explanation: Use the drawing to machine panel openings, follow the datasheet-specified tolerances, and apply a calibrated torque tool to the panel nut; avoid over-torquing and verify mating depth to prevent contact damage.
Materials, finishes, compliance and reliability notes
Point: Contact plating and body materials determine conductivity and corrosion resistance. Evidence: Datasheet lists contact finish and material treatments plus RoHS status and operating temperature. Explanation: For outdoor use, confirm plating and sealing level, prefer corrosion-resistant finishes, and plan for periodic inspection in corrosive environments to maintain low-loss performance and lifespan.
4 — Applications and compatibility (case study / examples)
Typical use cases with configuration examples
Point: 7/16 jacks are used where high power and low intermod are needed. Evidence: Common examples include base-station combiners, tower feedlines and broadcast transmitter panels. Explanation: In a combiner rack, a 7/16 jack reduces intermod and manages higher RF currents versus smaller connectors; specify complementary flanges and adapters to match your feedline geometry.
Comparison vs. alternative connectors
Point: 7/16 vs N-type vs 4.3-10 tradeoffs center on power, size and cost. Evidence: 7/16 form-factor typically offers higher power handling and lower intermod than N-type, while 4.3-10 provides a compact, modern low-PIM alternative. Explanation: Select the 60K131-815N1 when power handling and legacy rack compatibility outweigh savings in size or cost from smaller connectors.
5 — Procurement, installation checklist & troubleshooting (action)
Where to buy, part variants and lifecycle info
Point: Verify sourcing and version suffixes before purchase. Evidence: Datasheet and authorized distribution metadata identify active/obsolete status and variant suffix meanings. Explanation: Buy from authorized suppliers, confirm the exact part number and datasheet revision, and request traceability documentation to ensure authenticity and correct finish/variant.
Quick install checklist and common failure modes
Point: A short checklist prevents common installation issues. Evidence: Failures like poor VSWR usually stem from bad mating, damaged contacts or incorrect torque. Explanation: Checklist — verify PN, inspect finish, use correct panel cutout, apply calibrated torque, retest S-parameters post-install; troubleshoot by cleaning contacts, remating with proper torque, and re-measuring S11/S21.
Summary
The Rosenberger 60K131-815N1 is a 50 Ohm 7/16 jack rated DC–7.5 GHz; it suits high-power, low-intermod RF links in telecom and broadcast. Key reasons to choose it include robust power handling and stable RF performance—always download and verify the official datasheet and confirm specifications with your supplier before acceptance.
Key summary
- The 60K131-815N1 is a 50 Ohm 7/16 straight jack rated DC–7.5 GHz; use for high-power, low-intermod feedlines and combiners (check datasheet for S-parameter plots).
- Extract return-loss/VSWR and insertion-loss points from the datasheet for your operating frequencies and use the maximum values for worst-case budgeting.
- Follow dimensional drawings and manufacturer torque guidance when panel-mounting; verify RoHS, contact finish and sealing level for outdoor reliability.
FAQ
What is the 60K131-815N1 frequency range and impedance?
Answer: The 60K131-815N1 is specified for 50 Ω systems and a frequency range from DC up to 7.5 GHz in the official datasheet. Engineers should extract specific S-parameter points from the datasheet plots at their operational frequencies to confirm insertion loss and return loss for the application.
How should I verify RF performance after installation of this 50 Ohm 7/16 jack?
Answer: Verify by measuring S11 and S21 with a calibrated network analyzer across the intended band, confirm VSWR and return loss meet system margins, and retest after final torque and environmental sealing. Compare measured curves to the datasheet’s typical and maximum traces for acceptance.
What are common causes of poor VSWR with this connector and how do I troubleshoot?
Answer: Common causes include improper mating, damaged contacts, incorrect panel cutout or wrong torque. Troubleshoot by inspecting contacts, remating with the correct mating connector, using a calibrated torque wrench, cleaning corrosion or debris, and re-measuring S-parameters to isolate the fault.
- Technical Features of PMIC DC-DC Switching Regulator TPS54202DDCR
- STM32F030K6T6: A High-Performance Core Component for Embedded Systems
- APT50GH120B Datasheet Deep Dive: Specs, Ratings & Curves
- APT50GH120BSC20 Power Module: Latest Performance Report
- APT50GH120BD30 IGBT: How to Maximize Efficiency for EV Drive
- GTSM20N065: Latest 650V IGBT Test Report & Metrics
- CMSG120N013MDG Performance Report: Efficiency & Losses
- GTSM40N065D Technical Deep Dive: 650V IGBT + SiC SBD
- NOMC110-410UF SO-16: Live Stock & Price Report
- 1757255 MSTBA 5.08mm PCB: Step-by-Step Install & Solder
-
 EXB-V4V120JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 12 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V120JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 12 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V473JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 47K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V473JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 47K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V823JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 82K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V823JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 82K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V151JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V151JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V181JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 180 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V181JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 180 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V331JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 330 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V331JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 330 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V152JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 1.5K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V152JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 1.5K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V563JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 56K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V563JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 56K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V104JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 100K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V104JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 100K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V154JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V154JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150K OHM 0606