-
- Contact Us
- Privacy Policy
- term and condition
- Cookies policy
BMA connector 1785-6001-TD: Current Stock, Specs & Test Data
Recent inventory snapshots and RF test logs indicate rising demand for BMA connector types rated to 18 GHz, with lead-time swings that can disrupt RF module builds and certification timelines. This article examines procurement signals, detailed specs, and representative test guidance for the 1785-6001-TD, and provides a practical validation checklist engineers and buyers can use to protect schedules and performance. The focus is technical but practical for RF engineers, procurement managers, and PCB designers in the US market; it also highlights key specs to confirm before purchase.
Background

Form factor & intended applications (1)
The 1785-6001-TD is a BMA connector in a 50-ohm family intended for compact RF assemblies. As a male PCB thru-hole BMA option, it is optimized for space-constrained modules, test fixtures, and short antenna interconnects where repeatable mating and low profile are priorities. The part suits assemblies that require a reliable snap-on mating and consistent RF performance across the designated frequency range; designers should confirm board stack and clearance when choosing a thru-hole BMA footprint.
Why engineers choose this part (2)
Designers often select this BMA connector for its compact footprint, reliable snap engagement, and suitability for moderate-frequency RF subsystems. It offers a balance between mechanical robustness and small size compared with heavier SMA-like interfaces. Trade-offs include slightly lower mechanical torque margins versus threaded connectors, so engineers prioritize stable mounting and controlled mate/unmate procedures when designing for repeated service or field connections.
Data Analysis
Inventory snapshots & lead-time indicators (1)
Interpreting 1785-6001-TD current stock requires tracking in-stock quantities, typical pack sizes, and rolling lead-time estimates from authorized channels. Weekly snapshots reveal trends: small, intermittent in-stock lots indicate constrained supply, while steady multi-thousand-piece availability signals stable supply. For production planning, calculate safety stock based on average weekly consumption and typical lead-time variance; monitor authorized-channel snapshots and set reorder triggers when available inventory falls below two to three weeks of demand.
Pricing trends & procurement risk signals (2)
Price volatility, MOQ tiers, and packaging modes (tray versus bulk) flag procurement risk. Actionable thresholds: place orders or secure allocation when lead-time exceeds eight weeks or when 30‑day price increases exceed 8–12%. Capture a 90‑day rolling price/availability trend to detect tightening; if MOQ forces oversized buys, compare carrying cost versus expedited lead-time impact to decide whether to hold buffer stock or qualify an alternative.
Specs Deep-Dive
Electrical specs to verify (1)
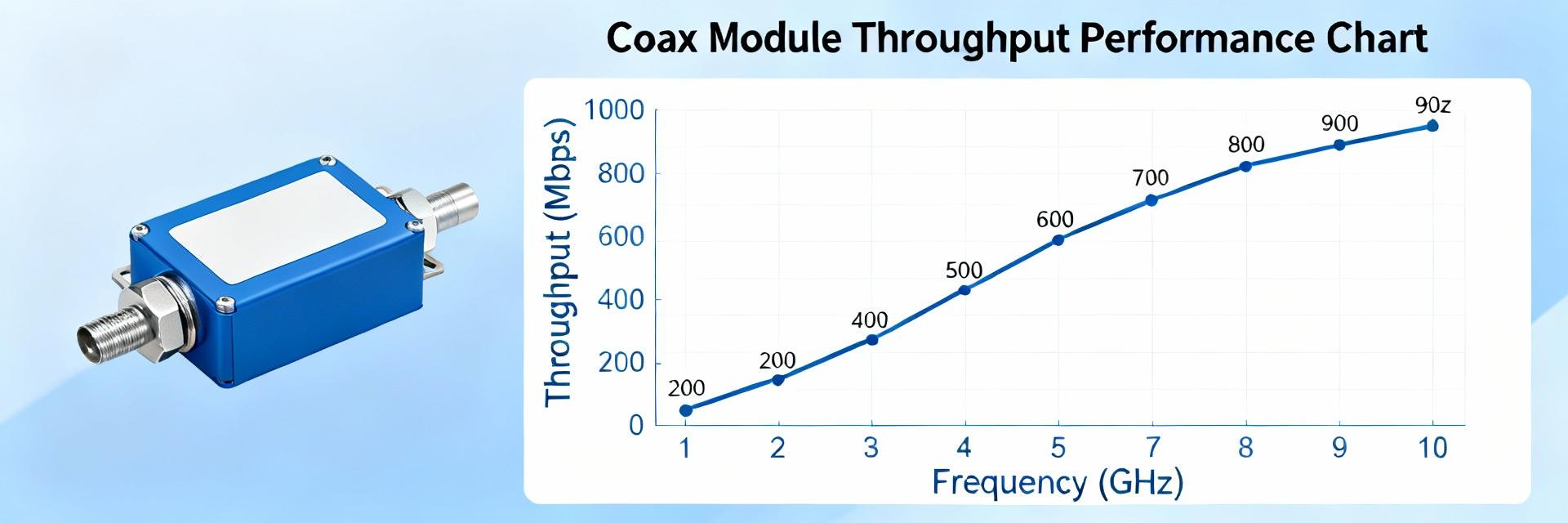
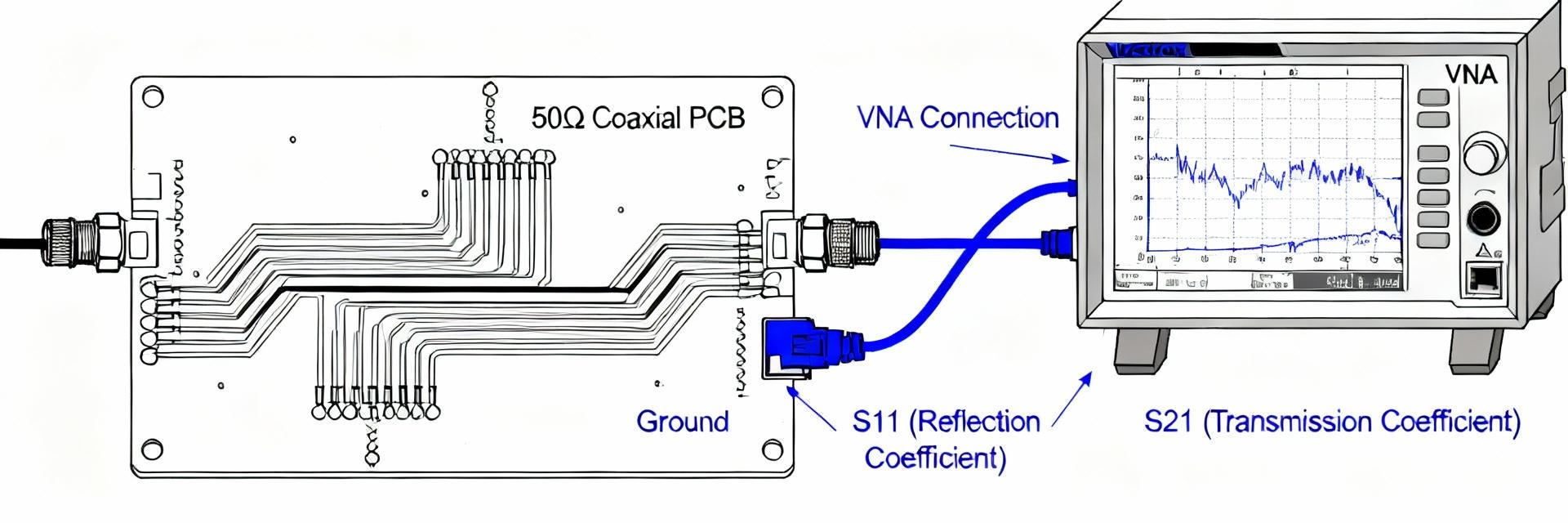
When reviewing BMA connector specs, verify 50-ohm nominal impedance, stated upper frequency rating, VSWR/return loss, insertion loss, dielectric withstanding voltage, and contact resistance. Suggested acceptance limits for typical RF subsystems: VSWR <1.3 across the intended band, insertion loss <0.2 dB at low GHz, and contact resistance in the low milliohm range. Cross-check datasheet curves against measured S11/S21 to confirm produced units meet published performance under real-fixture conditions.
Mechanical & footprint specs (2)
Confirm mating style (male thru-hole), plating option (tin, nickel, or specified finish), exact through-hole pad dimensions, and recommended land pattern. Verify mate/unmate durability (cycles) and mechanical retention parameters. Reference the connector mechanical drawing tables for hole size, plating thickness, and seating height; ensure the PCB footprint in the CAD library matches the drawing to avoid misalignment and assembly rework during volume production.
Test Data & Performance
Typical RF test results to request or run (1)
Request S-parameter data (S11 and S21) across the target band and run insertion loss, return loss, and phase stability tests on sample parts. Use a matched test fixture to avoid measurement artifacts: short pcb traces, controlled launch geometry, and calibrated fixtures are essential. Bench benchmarks: expect VSWR <1.3 up to the rated frequency and insertion loss consistent with datasheet curves; flag any sample that deviates by more than 0.2 dB from published S21.
Environmental & reliability tests (2)
Key reliability checks include thermal cycling, shock and vibration, humidity/condensation exposure, and mate/unmate endurance. Accelerated expectations vary by application: 100–500 thermal cycles for industrial use, and derived salt-spray or humidity soak if external connectors are exposed. Acceptance criteria should include maintained electrical continuity, no plating degradation, and retention of RF performance within predefined deltas after environmental stress.
Actionable Checklist
Pre-purchase verification checklist (1)
Before ordering 1785-6001-TD, confirm the exact part number and plating option, request the latest datasheet and S-parameter reports, verify footprint compatibility in CAD, obtain sample units for RF spot-checks, and confirm lot traceability and RoHS compliance. Use a simple procurement decision matrix weighing stock versus lead-time versus price: prioritize sample testing and allocate buffer stock if lead-time exceeds the project’s slack window.
Alternatives & PCB assembly considerations (2)
When identifying drop-in alternatives, match electrical specs, mating style, and PCB footprint precisely. For thru-hole BMA soldering, follow recommended soldering profiles, allow for post-solder cleaning, and account for potential reflow restrictions. Validate any substitute in a short RF test plan to confirm EMC-sensitive products remain within certification limits without a full validation cycle.
Key Summary
- Verify core BMA connector electrical specs — 50-ohm impedance, VSWR limits, and S-parameter alignment with datasheet before acceptance.
- Monitor 1785-6001-TD current stock and 90-day price trends; reorder when lead-time or price thresholds indicate tightening to avoid production delays.
- Run S11/S21 checks on samples and basic environmental cycles; confirm mechanical footprint and plating to prevent assembly issues.
Common Questions
Is 1785-6001-TD suitable for high-frequency designs?
Yes — the 1785-6001-TD is specified for BMA-class applications and is intended for high-frequency use within its published upper GHz limit. Designers should validate sample S-parameters in their fixture to ensure VSWR and insertion loss meet system-level budgets across the intended band.
How should teams monitor 1785-6001-TD current stock for production planning?
Establish weekly inventory snapshots from authorized channels, capture 90-day availability and price trends, and set reorder triggers based on two to three weeks of supply. If lead-time spikes or price increases beyond your threshold, secure buffer stock or allocation to protect critical builds.
What minimal tests should be run on 1785-6001-TD samples before acceptance?
At minimum, request S11/S21 sweeps in a matched fixture, a mate/unmate endurance check, and a short thermal cycle relevant to the product class. Confirm electrical deltas versus datasheet curves and ensure mechanical mounting fits the PCB footprint to avoid later failures.
Summary
To deploy the BMA connector successfully, engineers must verify electrical specs, confirm mechanical footprint and plating, and monitor stock and price trends to avoid production interruptions. For 1785-6001-TD, request S-parameter reports, run basic environmental and mate/unmate tests on samples, and maintain rolling availability snapshots. Pragmatic next steps: download the latest datasheet, perform a focused RF test on samples, and schedule weekly procurement reviews to manage lead-time risk.
- Technical Features of PMIC DC-DC Switching Regulator TPS54202DDCR
- STM32F030K6T6: A High-Performance Core Component for Embedded Systems
- APT50GH120B Datasheet Deep Dive: Specs, Ratings & Curves
- APT50GH120BSC20 Power Module: Latest Performance Report
- APT50GH120BD30 IGBT: How to Maximize Efficiency for EV Drive
- GTSM20N065: Latest 650V IGBT Test Report & Metrics
- CMSG120N013MDG Performance Report: Efficiency & Losses
- GTSM40N065D Technical Deep Dive: 650V IGBT + SiC SBD
- NOMC110-410UF SO-16: Live Stock & Price Report
- 1757255 MSTBA 5.08mm PCB: Step-by-Step Install & Solder
-
 EXB-V4V120JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 12 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V120JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 12 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V473JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 47K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V473JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 47K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V823JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 82K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V823JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 82K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V151JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V151JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V181JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 180 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V181JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 180 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V331JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 330 OHM 0606
EXB-V4V331JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 330 OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V152JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 1.5K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V152JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 1.5K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V563JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 56K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V563JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 56K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V104JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 100K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V104JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 100K OHM 0606 -
 EXB-V4V154JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150K OHM 0606
EXB-V4V154JVPanasonic Electronic ComponentsRES ARRAY 2 RES 150K OHM 0606